Kyle Hankins, CTO and co-founder of Bytewhisper Security, thought he’d hit the jackpot.
The engineer he interviewed knew the stack inside and out. Clean code samples. Great communication. References that checked out.
But during the hiring process, something felt off. The candidate aced the interview on Zoom until Bytewhisper’s deepfake detection technology flagged him as a fake. Hankins wasn’t alone.
Vijay Balasubramaniyan, CEO of Pindrop Security Solutions, faced the same issue with a remote engineering hire.
Matt Moynahan, CEO of GetReal Security, has also warned publicly about similar incidents.
These leaders realized how easy it is for startups to fall for candidates who look perfect on paper but turn out to be complete risks in execution.
And this is just the tip of the iceberg.
CB Insights looked at 483 startup failures and found that 92% of startups fail.
But nearly 37% of those failures trace back to technical team issues. Bad devs don’t just waste your money. They wreck your timeline. They wreck your reputation. They ruin your chances of raising the next round.
In 2025, with AI raising expectations and funding harder to get, one bad hire can sink your company.
Here’s what you might be going through right now:
“My app works in demos, but crashes under load.”
“Features are overlapping, missing, or delayed.”
“The person I trusted isn’t available when I need them — or avoids calls or meetings.”
“I keep paying for code that feels brittle or untested.”
“Investors are asking for stable demos, but what I have isn’t ready.”
By the end of this article, you’ll know exactly how to spot these startup killers before they destroy everything you’ve built.
The Hidden Cost of Bad Developers (More Than Just Money)
The Financial Devastation
Bad development work wastes your budget. Worse: it destroys value you hoped to build.
- Founders often spend $50K-$200K before realizing delivery, code quality, or architecture is failing.
- Then rebuilds or rewrites can cost multiples of that.
- Plus you may need to patch security holes, fix performance issues, or deal with customer complaints.
A Reddit post titled “I wasted $50,000 building my startup…” tells how a non-technical founder first hired a reliable Pakistani web dev.
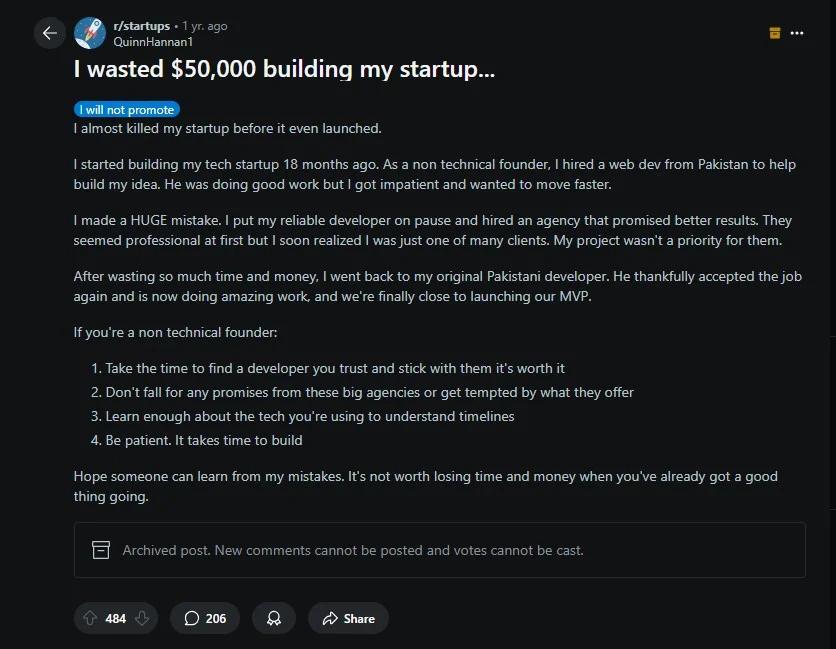
Then switched to an agency promising faster, more polished work. The agency failed to prioritize the project. The original dev was rehired.
The MVP is now close. But the extra cost, time, and loss of trust burned months of runway.
The Time Trap
Time lost is often more damaging than money lost.
- Delays in product launches give competitors room to steal your ideas or audience.
- Founders spend time babysitting devs, fixing crap, redoing work.
- These delays stretch runways, cause missed market windows, and drain morale.
From the same Reddit thread above: what should have taken months became 18 months of stops, rewrites, and confusion. That gap made fundraising harder and downstream features cost more.
The Reputation Damage
A buggy product or missed promises doesn’t just cost users. It costs your credibility.
- Early users post bad reviews; word spreads.
- Investors see instability at demo, lose confidence.
- Internally, teams burn out. Founders second-guess hires.
If people think you can’t deliver quality or be reliable, they won’t bet on you. And once reputation is damaged, repairing it costs more time and money than building from clean foundations.
Red Flag #1 — The Moonlighting Menace
“Moonlighting” here means working for more than one company at once, without being transparent. Not just freelancing on the side, but taking roles that interfere with availability, quality, and commitment.

Soham Parekh’s case shows how hidden commitments can seem invisible until they cause missed deadlines, conflicting work, or breakdowns. Interviews go great. Post‐hire, things wobble. Tasks lag. Delivery slips.
Why It’s More Common Than You Think
- Remote work makes it easy to hide multiple commitments.
- Many developers take side gigs for income. Some agencies allow or ignore it.
- Founders often don’t ask or enforce exclusivity, especially early.
Warning Signs to Watch For
- Inconsistent availability during your working hours.
- Urgent issues linger while slack messages / tickets go unanswered.
- Quality declines over time.
- Communication becomes templated or generic.
- Reluctance to join video calls, standups, collaborative sessions.
The Real Impact
Founders have reported that when they found out a supposed dedicated dev was actually spread over several projects, things fell apart:
- Missed deadlines.
- Security or IP issues (repos mixed, confidentiality risk).
- Code quality suffering as dev tries to juggle tasks.
One Reddit thread (r/startups) reports a founder rehired an original dev after a failed agency engagement, noting how much smoother things got when someone was committed and consistent.
Red Flag #2 — The Proxy Hiring Scam
This is when someone else (coach, senior person, interview “ringer”) handles interviews or architecture, but the actual work is done by a lower-skill person. Or multiple people, via outsourcing, without you seeing it.
Delayed delivery, low test coverage, mismatched communication often follow.
How Proxy Hiring Works
- Expert handles interview; junior delivers.
- Agency or middleman shows senior experience, but actual coding is junior level.
- Sometimes identity/location claims are misleading (e.g. “US time zone” but unavailable then).
Detection Techniques
- Compare what was promised in interview vs what code you get: maintainability, modularity, test coverage.
- Watch for shifts: confident explanation in interview, then vague responses or delays later.
- Ask follow-up architectural or design questions months in.
- Check commit history, code ownership, comment style.
Real-World Example
In a Reddit discussion, a founder said they were misled by excellent interview architecture discussion, but post-hire the code was untested, messy, and the developer avoided difficult questions.
They later realized the interview “senior” was not involved in most delivery. This mismatch cost them trust, time, and forced architecture rewrites.
Red Flag #3 — The Overstaffing and Overbilling Trap
Some vendors propose big teams with many specialists even when the project doesn’t need them. It looks impressive in proposals. But more people often introduce more complexity, delays, and cost.
Common Overstaffing Tactics
- Assigning specialists for every micro-task.
- Senior titles hiding junior execution.
- Artificial dependencies: roles waiting on other roles, meetings, oversight.
Financial Impact Analysis
A Quora or Reddit case: founder hired a 7-person team (front-end, back-end, UI, UX, DevOps, QA, PM) for what should have been a lean web app.
After auditing, they found only 2-3 people were producing meaningful code; others were blocked, in meetings, or managing tasks that didn’t add value.
Their invoice over 3 months was much more than a small skilled team could have done. The overhead killed speed and cost.
The Lean Team Advantage
Lean teams force clarity: each person owns something real. Fewer dependencies mean fewer delays. Fewer people to coordinate. Better feedback loops. Faster iteration.
Red Flag #4 — The Communication Black Hole
When Developers Go Dark
One of the earliest signs that something is wrong: communication slips. Not always obvious at first.
Status Update Manipulation & Progress Inflation
- “Everything’s on track.”
- “Good progress.”
- Lack of working demos or measurable output.
These often mask actual delays or missed scope.
Warning Signs
- Meetings canceled or rescheduled often.
- No screen shares or work-in-progress shown.
- Missing deadlines without heads-up.
- Avoidance when asked about blockers or specific issues.
The Trust Erosion Cycle
Trust is fragile. When you don’t get clarity, you start micromanaging. Developers feel pressure, hide errors. Communication gets defensive. Small slips become bigger gaps. The project suffers, morale drops.
One founder on Reddit said: after 8 weeks of weekly updates, they realized their dev was showing mockups or UI placeholders rather than working backend features.
They thought they were close to MVP. They weren’t. The mismatch between promised features and deliverables cost them investor interest.
Red Flag #5 — The Technical Debt Time Bomb
Understanding Technical Shortcuts
Sometimes you need speed. But if you build too many shortcuts — skip tests, ignore documentation, delay refactoring — debt piles up.
Why “Move Fast” Might Move You Backward
What starts as fast MVP often becomes messy when users increase, traffic rises, or new features are added. The foundation cracks. Changes cost more. Bugs multiply.
Early Warning Signs
- Bugs increase faster than feature gains.
- Sprints that used to take 1 week now take 3.
- “It works on my machine” becomes excuse.
- Minimal tests, missing docs.
- Feature patches over architecture rather than rebuild.
Long-Term Consequences
- Scaling problems, slow performance.
- Security vulnerabilities.
- Rewrites become inevitable, huge cost.
One Reddit thread from r/ExperiencedDevs last year tells about a startup that patched and patched their backend until things broke — needing a full rewrite.
Rebuild took 4 months and cost more than what they’d originally spent building the buggy version.
The Psychology Behind These Failures
These problems don’t just happen because of bad code or bad luck.
They happen because of what people believe, what they feel, and what they let slide. Understanding the psychology helps you catch issues before they cost you.
The Technical Knowledge Gap
If you're non-technical, it’s hard to distinguish polished slides from solid architecture. Portfolios, testimonials, interviews can be impressive even if the underlying code is brittle.
Without enough understanding, you may not notice big risks until they manifest. And by then, time and money are lost.
Desperation and Time Pressure
When runway is short, or investors expect something fast, founders cut corners. They may hire quickly without vetting, skip documentation, postpone testing. The urgency feels real. But it often causes problems later.
The Lowest-Bidder Mentality
Going with the cheapest option feels like winning up front. But then “cheap” often means under-resourced, under-experienced, or overpromised.
Founders often think they can fix things later. Many Reddit threads from 2024-2025 reflect regret over choosing low bids only to face delays, poor code, or needing replacement.
Over-Reliance on Portfolios & Testimonials
People tend to assume past performance equals future result. But portfolios often highlight wins, not the breakdowns.
Testimonials often mask behind what was promised vs delivered. A dev may have built cool side projects but under-deliver in critical parts of your product.
The Trust-but-Don’t-Verify Problem
You want to trust. But trust without verification leads to blind spots.
- Not seeing interim deliverables.
- Not inspecting code or reviewing architecture.
- Accepting vague promises.
Fix: demand smaller proofs early. Insist on working features over perfect promises.
The Prevention Framework — How to Protect Your Startup
Here are concrete tools and processes you can use to prevent the $500K mistake. These help you ensure the problems above don’t take root.
Due Diligence 2.0
Before hiring or contracting:
- Give real tasks that reflect your product’s complexity. This shows how someone handles things under constraints.
- Review code samples or open source work. Ask not just “Did they build it?” but “How did they build it? What trade-offs they made?”
- Talk to recent clients or coworkers. In particular, ask about timelines, missed deadlines, code refactoring, how devs dealt with scaling.
- Check claimed location, working hours, prior commitments. If someone says “US hours”, test that early.
Contract and Legal Protections
Startups often skip these early, thinking contracts are overhead. They aren’t.
- Add IP ownership clauses. All work, documentation, repos need to be contractually yours.
- Include exclusivity or moonlighting policies. Be explicit about side projects.
- Use milestone-based payments. Only release payment when deliverable meets your standard.
- Define termination and handover: what happens if things don’t go well or you need to switch devs.
Ongoing Monitoring Systems
Once you work together, don’t assume everything will always go well.
- Use code quality tools (linters, static analyzers, test coverage). Look at patterns: lots of bugs, missing docs, failing tests.
- Have frequent review cycles: working demos every 1-2 weeks. You need to see something you can use or test.
- Use transparent dashboards: commits, bugs fixed, features done, code review status. Avoid “trust me” updates.
- For critical parts (security, payments, user data), bring in third-party audits early rather than waiting for crisis.
How Over-Communication Is Necessary
Over-communication is often seen as annoying, but in dev partnerships, it’s essential.
- Set norms: daily or frequent updates. What was done, what’s next, what’s blocking.
- Use working artifacts: screen shares, demo builds, video walkthroughs. Don’t accept vague reports.
- Encourage early disclosure of issues. If something’s going to slip, better to know early than be surprised.
- Clarify expectations: quality, test coverage, deadlines, documentation. Be explicit, not assume.
When communication is strong, you catch small issues before they become disasters. Teams stay aligned. Trust builds. Scope creep is controlled.
Building a Reliable Development Partnership
You don’t want just a developer. You want a partner who understands your product, cares about quality, and protects your interests.
The Agency vs. Freelancer Decision Matrix
- Freelancers: flexible, sometimes cheaper. Good for discrete tasks. Risks include availability, dependency, consistency.
- Agencies: offer structure, backup resources, sometimes more polish. But you must verify who is actually working (senior? junior?), avoid overstaffing and hidden juniors.
- Hybrid Models: great mix. Core dependable dev(s) + specialized help if needed. Helps maintain consistency and control while scaling.
Key Questions to Ask Potential Partners
Before signing anything, consider asking:
1. Who will write the code? Can I meet the person(s) directly?
2. Are they working on other projects? What’s their availability?
3. What if someone stops contributing or leaves? What’s the replacement process?
4. Can I see code from similar past projects? How did they deal with bugs, scaling, security?
5. How will ownership of code, IP, and confidentiality be handled?
6. What metrics will you report (bugs, uptime, speed, quality) and how often?
7. What is the schedule of deliverables and demos?
Establishing Successful Working Relationships
To keep things healthy:
- Set up communication protocols: frequency, format, tools. Clear modes for updates, blockers, feedback.
- Use milestone-based management: at each stage, you should see working software, not just designs.
- Build feedback loops: both you and the dev team should regularly discuss what’s working and what’s not.
- Check for cultural fit: timezones, expectations, language style, work ethic. These matter in remote work.
- Start small: begin with a trial project or small deliverable. If that goes well, scale responsibilities.
How epicX Eliminates These Risks
epicX was founded to avoid exactly the kind of disasters we’ve been talking about. Here’s how:
- A rigorous 4-stage vetting process: technical assessments with real-world project simulations; background verification to eliminate proxy hiring; cultural-fit evaluation to ensure communication is strong.
- Trial periods with gradually increasing responsibility. You see early what a dev can really do.
- Exclusive developer agreements. When contracted, our devs commit to working only on your project during that period—no undisclosed side work.
We use a dedicated team model. The same people work through your product phases. You don’t get rotating faces or hidden handovers. Consistency matters.
Transparency and Communication Excellence
To stay aligned, we commit to:
- Weekly progress reports with meaningful metrics, not vague promises.
- Direct access: you talk to project leads, devs, and managers, not just gatekeepers.
- Real-time dashboards showing code commits, bugs resolved, feature progress.
We also support escalation: urgent issues can be flagged, problems discussed early.
Mandatory demos every two weeks mean you see working software, not presentations. If something’s off, you discover early.
Quality Assurance and Long-Term Partnership
Quality isn't an afterthought. It is baked in.
- Code reviews happen before anything goes to production.
- Technical debt prevention is part of every cycle—refactoring, test coverage, documentation.
- Scalability planning starts with your first features, not after you outgrow your system.
And because we believe in continuous improvement, we optimize team skills and structures as your needs grow.
Your Next Steps to Development Success
You’ve seen how real founders get burned by bad dev partnerships. You’ve read real threads, real mistakes, real costs. But you also now have a map: red flags, psychology, prevention, partnership.
Here’s what to do right now:
- Look at your current dev setup. Are there red flags? Moonlighting, proxy hiring, over-billing, communication gaps, technical debt growing?
- If hiring, use the prevention frameworks above. Demand working proof, clear contracts, frequent demos.
- If things are already slipping, don’t wait. Review, possibly switch partnerships, audit the code, set new expectations.
The difference between a startup that struggles and one that succeeds often isn't the idea. It’s who builds it and how.
Don’t let the $500K mistake be your path. Learn, inspect, act. You deserve a dev team that doesn’t just build your idea, they protect it.