TL;DR
- Trump's $100,000 H-1B fee starts September 21, 2025 - but only for NEW applications (existing holders safe)
- Initial panic spread as companies misunderstood policy scope - renewals and current workers unaffected
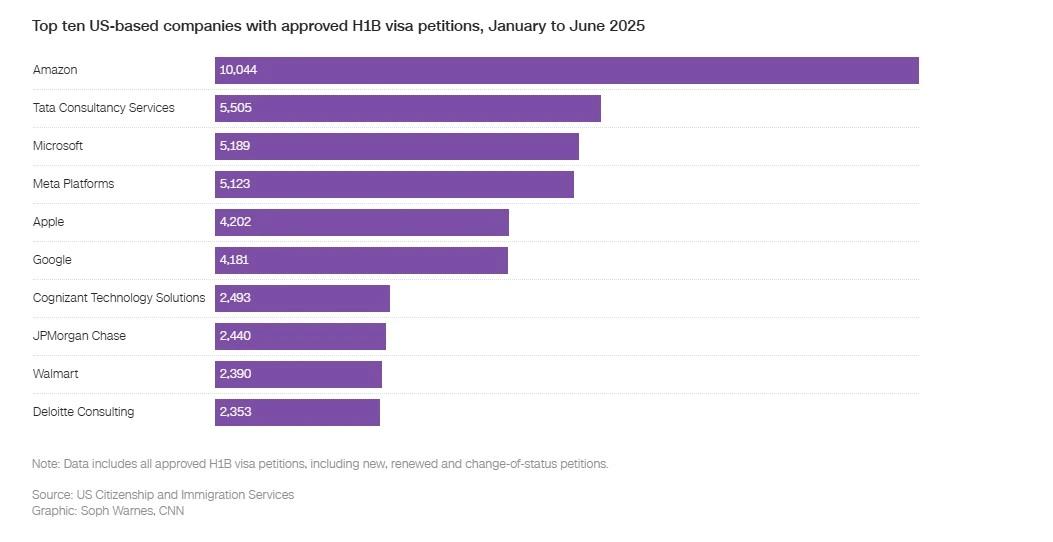
- Amazon tops the list with 10,044 H-1B approvals, Microsoft and Meta follow with 5,000+ each
- One-time fee targets corporate dependency on foreign talent, not individual workers
- Innovation and development work shifting to offshore markets as companies seek alternatives
- Demand for offshore development partners expected to surge as H-1B economics break down
- Indian IT professionals face biggest disruption as primary H-1B beneficiaries
- Remote-first and distributed team models gaining momentum across tech industry

If there was a toll booth for global talent, it just got sky high.
On September 21, 2025, President Trump’s administration confirmed a $100,000 filing fee for every new H-1B visa petition.
That number isn’t just a policy tweak. It’s a sledgehammer swung directly at how American tech companies have hired talent for decades.
The first reaction inside corporate boardrooms was chaos. Emails, emergency calls, late-night strategy meetings. Some workers feared their existing visas might be voided.
Others wondered if upcoming renewals were in danger. Eventually, clarifications came, but the sense of disruption didn’t fade. The ground rules for hiring in tech had shifted overnight.
For companies like Amazon, Microsoft, and Google, the math is brutal. Keeping the same hiring flow could now mean billions in added costs.
For startups, even a single visa might eat up an entire funding round. Suddenly, offshore teams, hybrid models, and distributed setups aren’t just options. They’re survival strategies.
So what happens when the world’s most expensive work visa becomes the price of entry for foreign talent? And where will the next wave of innovation take root if the US shuts the door this tight?
What is an H-1B Visa? America’s Shortcut to Global Tech Talent
For decades, the H-1B program has been America’s golden ticket for importing skilled talent.
Tech firms leaned on it heavily, using the system to bring in developers, engineers, and data scientists from around the world.
The setup was simple: companies could hire foreign professionals for specialized roles when they couldn’t fill them locally. The visa typically ran for three years, extendable to six, with many workers eventually transitioning into permanent residency.
The H-1B became so central that it shaped entire hiring pipelines. Recruiters scouted globally with the expectation that the visa process, while competitive, was financially manageable.
With the fee now raised to $100,000, that “shortcut” suddenly feels like the most expensive detour in corporate history.
Other popular US work visa options include:
- L-1 Visa: For employees transferring within the same multinational company.
- O-1 Visa: For individuals with extraordinary achievements in their field.
- TN Visa: For Canadian and Mexican professionals under trade agreements.
- E-2 Visa: For investors and employees of treaty countries.
- F-1 OPT: Training work permits for international students.
- J-1 Visa: For researchers, interns, and cultural exchange participants.
Why This Decision Sends Shockwaves Through Corporate America
This isn’t the kind of policy update that slips quietly into a footnote. The $100,000 H-1B fee is a reset button on how American companies bring in foreign talent, and the fallout is already being felt across the industry.
The economics alone are jaw-dropping. What once cost a company around $10,000 per hire now comes with a six-figure price tag.
For Amazon, which filed more than 10,000 petitions in the first half of 2025, that translates into more than a billion dollars in fees. And that’s before even counting legal costs or the uncertainty of approvals.
The real punch, though, is in the timing. Tech firms are already dealing with shortages in fields like AI, cybersecurity, and advanced engineering.
Years of careful recruitment strategies built around the H-1B pipeline have been wiped away in a single policy move. Now, companies that relied on this flow of talent are scrambling to rebuild their hiring playbooks.
It isn’t just the giants rethinking strategy. Startups that once counted on one or two key H-1B hires are realizing those costs could consume entire seed rounds.
Venture investors are starting to ask blunt questions about hiring plans. Expansion plans that were slated for the US are being shifted abroad. The shockwaves ripple from boardrooms in Silicon Valley to venture meetings in New York.
Read More: 9 Reasons Why Pakistan Is the Go-To Choice for Tech Talent Sourcing in 2025
Breaking Down the $100K Reality: What Actually Changed
The initial rollout of the policy sent corporate America into a frenzy.
Internal advisories, all-hands calls, and weekend strategy sessions dominated the days after the announcement. Social media buzzed with rumors: Would current visa holders be kicked out? Were renewals suddenly at risk? The noise was deafening.
But after the dust settled, the details became clearer. Here’s the reality companies now face:
The Fee Structure
- Old cost: roughly $5,000 to $10,000 per petition
- New rule: $100,000 plus all standard processing fees
- Timing: Payment is due at the time of filing, not after approval
- Type: A one-time charge, not a recurring annual payment
The Scope Reality Check
The administration confirmed that existing H-1B holders remain untouched. Renewals and extensions with the same employer still follow the old cost structure.
Travel and re-entry rights for current workers are unchanged. The fee only applies to new petitions filed after September 21, 2025.
The Target
The move isn’t aimed at individual workers. It’s aimed squarely at corporate hiring behavior. By slapping a six-figure fee on every new petition, the government is forcing companies to treat each H-1B decision as a serious budget call rather than a routine HR expense. In effect, it turns what was once an operational step into a strategic one.
The Ground Reality: By the Numbers
The data tells the real story of who's about to feel this policy shift most directly. Based on approved H-1B petitions from January to June 2025, here's the corporate landscape that just got turned upside down:
The Heavy Hitters
- Amazon: 10,044 approved petitions (potential $1+ billion annual fee burden)
- Tata Consultancy Services: 5,505 petitions
- Microsoft: 5,189 petitions
- Meta Platforms: 5,123 petitions
- Apple: 4,202 petitions
- Google: 4,181 petitions
The Supporting Cast
- Cognizant Technology Solutions: 2,493 petitions
- JPMorgan Chase: 2,440 petitions
- Walmart: 2,390 petitions
- Deloitte Consulting: 2,353 petitions
These numbers represent just six months of approvals. Annualized, we're looking at companies that would face hundreds of millions in additional costs to maintain current hiring practices.
The Math That Changes Everything
A mid-size tech company filing 50 H-1B petitions yearly now faces $5 million in fees alone. That's often more than their entire engineering budget. For startups, even a handful of international hires could consume their entire Series A funding.
The consulting firms face an even starker reality. Companies like TCS and Cognizant built their US business models around cost arbitrage - bringing skilled workers from India at competitive rates. A $100,000 fee per worker essentially eliminates that business model overnight.
The Immediate Stakes: Who Gets Hit First
Tech Giants Enter Crisis Mode
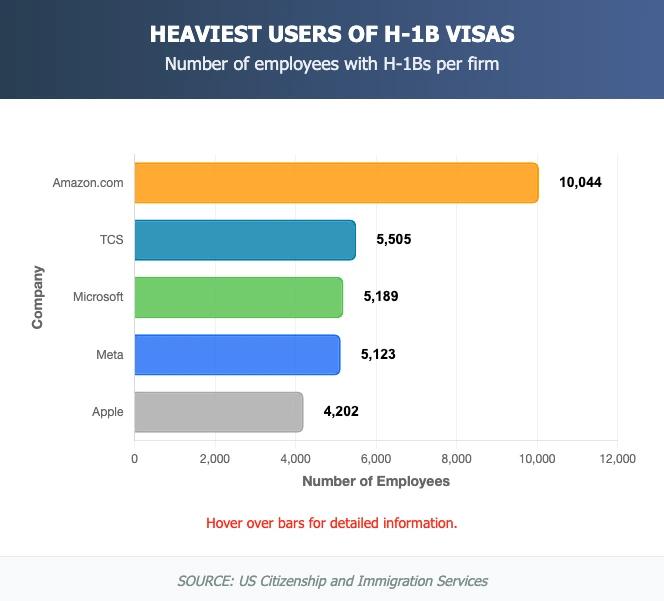
Amazon's situation illustrates the scale perfectly. Their 10,044 approvals in six months would translate to roughly $2 billion annually in visa fees alone. That's more than many companies' entire R&D budgets. Microsoft and Meta face similar math with their 5,000+ annual filings each.
These companies didn't just send routine HR updates to employees. They issued urgent advisories, activated legal teams, and started immediate strategic reviews of their global hiring practices. The panic was real because the financial impact is unprecedented.
Indian IT Services Hit the Wall
Tata Consultancy Services and Cognizant face existential challenges to their US operations.
Their entire business model relied on bringing talented developers from India to work on American projects. At $100,000 per visa, that model becomes economically impossible for most contracts.
These firms are already exploring massive pivots toward offshore delivery models and remote work arrangements. The days of flying teams to client sites in New York or Silicon Valley just ended for all but the highest-value engagements.
Startups and Scale-Ups Feel the Squeeze
A typical growing startup might need 10-20 international hires as they scale. That's now a $1-2 million decision just for visa fees.
Many will simply abandon international hiring altogether, while others are fast-tracking offshore development partnerships and international office setups.
Individual Professionals Face New Reality
Current H-1B holders remain completely protected, but aspiring applicants face a transformed landscape. Only companies with exceptional business justification will sponsor new H-1B workers. The days of speculative hiring or bringing over junior developers for training are over.
What Does This Mean for U.S. Tech Firms?
Strategic Recalibration Required
Tech companies now face fundamental questions they've never had to answer before. Which roles actually justify $100,000+ in visa costs? How do you maintain innovation pace when your talent pool just got 90% more expensive to access?
The companies adapting fastest are those treating this as an opportunity to build more resilient, globally distributed operations rather than just a cost problem to solve.
The Innovation Migration
Here's the unintended consequence nobody talks about: American companies are now setting up offshore innovation centers at record pace.
Why pay $100,000 to bring a machine learning expert to California when you can set up an entire AI research lab in Bangalore, Toronto, or London for less money?
Companies like Google and Microsoft already operate significant research facilities globally. This policy accelerates that trend dramatically, potentially moving cutting-edge innovation work outside US borders.
Competitive Dynamics Shift
Companies with existing offshore partnerships or remote-first cultures suddenly gained massive competitive advantages. They can access the same global talent pool without the visa lottery, fees, or geographic constraints.
Meanwhile, companies heavily dependent on H-1B co-location models face urgent strategic pivots. The winners will be those who can build effective distributed teams fastest.
The Ripple Effect: Industry-Wide Implications
Remote Work Gets a Policy Push
The policy inadvertently became the biggest catalyst for remote work adoption since COVID-19.
Companies that resisted distributed teams are now embracing them out of necessity. The infrastructure investments in collaboration tools, project management systems, and remote team culture are accelerating across the industry.
Global Tech Hubs Win Big
Countries like Canada, the UK, and Germany just became significantly more attractive for the same talent previously heading to the US. Their immigration systems, while not perfect, now offer dramatically better economics for both companies and workers.
Toronto, Vancouver, London, and Berlin are already seeing increased interest from both companies setting up offices and workers choosing alternative destinations. The global competition for tech talent just got a lot more interesting.
Educational Ecosystem Responds
American universities and coding bootcamps are seeing increased investment in domestic talent development programs. Companies that can't afford H-1B fees are doubling down on local talent pipelines, veteran retraining programs, and internal upskilling initiatives.
Impact on Indian IT Professionals and Global Talent Flow
The Primary Target Adapts
Indian professionals represent roughly 70% of H-1B beneficiaries, making them the most affected group. But they're not sitting still. The response has been swift and strategic.
Many are pivoting to Canadian immigration programs, European Blue Card systems, or remote work arrangements with US companies. Others are choosing to build careers in India's booming tech sector rather than navigate expensive US immigration pathways.
Brain Drain Reversal Accelerates
India's tech hubs were already attracting reverse migration as the domestic market matured. This policy accelerates that trend significantly.
Talented professionals who might have spent years trying to get to Silicon Valley are now choosing to build world-class companies in Bangalore, Hyderabad, or Mumbai.
New Career Pathways Emerge
The traditional path of H-1B to green card to American tech career is being replaced by more diverse options. Remote work with US companies while living in lower-cost countries. Starting companies in emerging markets. Building expertise in offshore development partnerships.
What Companies Should Do Right Now
Immediate Action Items
Every tech company needs to audit their current situation immediately. Review pending H-1B applications and calculate the budget impact. Identify which roles truly justify $100,000+ investment versus those that can be filled through alternative approaches.
The smartest companies are treating this as a forcing function to build better global operations, not just a cost problem to minimize.
Explore Alternative Visa Categories
L-1 visas for intracompany transfers become much more attractive when you can set up international offices. O-1 visas for exceptional talent remain viable for truly specialized roles. Some companies are restructuring their international operations specifically to enable these pathways.
Budget Reallocation Strategy
Instead of $1 million in H-1B fees, companies can build comprehensive offshore development partnerships, invest in remote work infrastructure, or establish international innovation centers. The math now favors distributed operations in ways it never has before.
Offshore Development and Global Teams: The New Competitive Advantage
The Economics Have Completely Flipped
A single H-1B visa fee of $100,000 can now fund an entire offshore development team for 6-12 months. Companies are discovering they can access the same talent pools through different geographic arrangements at a fraction of the cost.
The quality equation has changed too. Modern offshore development partnerships deliver not just cost savings but often improved development velocity through follow-the-sun development cycles and specialized expertise concentration.
Building Hybrid Excellence
The most successful companies are creating hybrid models that combine strategic onshore leadership with offshore development excellence. They're investing in the collaboration infrastructure, cultural integration, and project management systems needed to make distributed teams work seamlessly.
Cultural Fit and Technical Excellence
Today's leading offshore partnerships focus heavily on cultural alignment and communication excellence.
Companies like epicX have pioneered approaches that prioritize long-term partnership relationships over transactional cost savings, often resulting in development teams that integrate more effectively with existing operations than traditional H-1B hires.
These partnerships emphasize several key elements:
- Time zone optimization for real-time collaboration
- Advanced technical expertise in emerging technologies like AI and blockchain
- Integrated development processes with existing company workflows
- Cultural training and communication excellence programs
Success Stories in Action
Forward-thinking companies report that well-structured offshore partnerships often deliver better results than traditional co-located teams. They cite improved development metrics, 24/7 development cycles, and access to specialized expertise that's difficult to find domestically.
The key difference is approaching offshore development as a strategic partnership rather than a cost-cutting measure. When companies invest in proper integration, training, and long-term relationships, the results often exceed expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Does this $100,000 fee affect my current H-1B status?
Not at all. If you currently hold an H-1B visa, this fee has zero impact on your situation. You can travel internationally, renew your visa, extend your status, and even change employers (through amendment petitions) exactly as before. The fee only applies to completely new H-1B petitions filed after September 21, 2025.
Q: Is this fee charged annually or just once?
It's a one-time fee paid when filing a new H-1B petition, not an annual charge. However, if you change employers and they need to file a brand new petition (rather than an amendment), the new employer would pay the fee.
Q: Can my employer make me pay this fee?
No. US immigration law requires employers to pay all H-1B filing fees and related costs. They cannot require employees to reimburse them or deduct these costs from wages. Any employer asking you to pay H-1B fees is violating federal law.
Q: Will this reduce competition in the H-1B lottery?
Very likely. The high cost will discourage many companies from filing petitions, potentially reducing total applications significantly. This could improve approval odds for companies willing to pay the fee, though the overall number of approvals will probably drop substantially.
Q: What happens to applications already filed before September 21, 2025?
Applications filed before the effective date are completely exempt from the $100,000 fee, regardless of when they get processed or approved. Only new applications filed on or after September 21, 2025 face the fee.
Q: Can companies challenge this policy in court?
Legal challenges are possible and likely. However, companies should plan assuming the policy remains in effect. The policy includes a one-year expiration clause, but extensions seem probable given the administration's stated goals.
Q: How does this compare to other countries' work visa fees?
This makes US H-1B visas among the world's most expensive work permits. Canada's work permits cost under $500, UK Skilled Worker visas run around $2,000, and most European work permits range from $100-$1,000. The US fee is now 50-100 times higher than comparable programs.
Q: Will this apply to universities and non-profits?
The current policy doesn't specify exemptions for cap-exempt employers like universities and non-profits, though they may seek clarification. These organizations typically file far fewer H-1B petitions than private companies, so the impact would be more manageable even if the fee applies.
Q: Are there any exceptions or waivers available?
The initial policy announcement doesn't include exceptions or waiver provisions. Companies in all industries face the same fee structure regardless of size, revenue, or social impact.
Q: What about H-4 dependent visas for spouses and children?
The policy specifically targets H-1B work visas. H-4 dependent visa processes, fees, and benefits (including work authorization for eligible spouses) remain completely unchanged.


